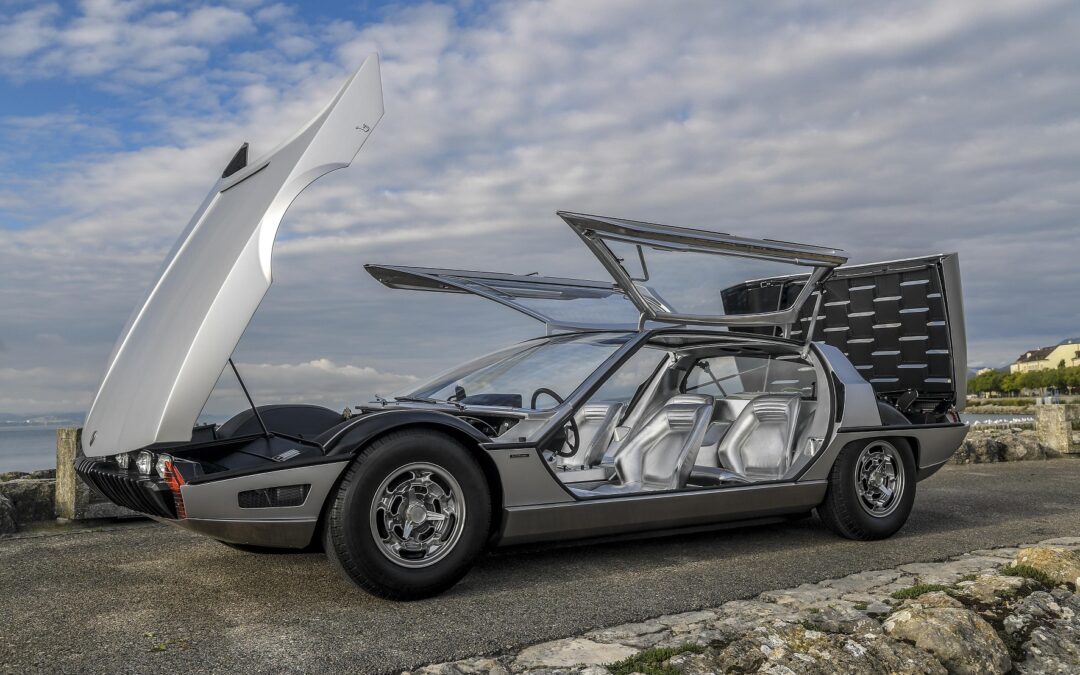
The 1967 Lamborghini Marzal concept car is distinctive for its expansive glass roof, spanning 48.4 square feet

The four-seat Lamborghini Marzal was created as a concept for a true four-seat grand-tourer. (Photos courtesy of Lamborghini)
The 1967 Lamborghini Marzal was a one-off show car that became a worldwide icon of style and design. The ultramodern four-seat Marzal was designed by Marcello Gandini for Carrozzeria Bertone https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gruppo_Bertone
Among its many special design elements were:
- An interior upholstered in silver-colored leather;
- A hexagonal central design theme. The geometric shape was repeated in the dashboard, the rear window, and in the console cut-out;
- 6 narrow S.E.V. Marchal headlamps in the thin, wedge-shaped nose;
- The extensive glass surface covers 4.5 square meters, reaching from the gullwing doors to the roof.
Lamborghini calls the Marzal “a fully operational show car with the largest glass surface in history.”

The central design theme for the Marzal centered around the hexagon.
4 Seat Grand Tourer
Lamborghini president Ferruccio Lamborghini had the Marzal created as a concept for a true four-seat grand touring car. In his lineup already were the 400GT 2+2 and the Miura.
The Marzal remained a one-off, though the general shape and many of the ideas would later be used in the Lamborghini Espada.
According to the Marzal page in Wikipedia, Ferruccio Lamborghini initially viewed the creation of the Marzal as advertising rather than a production model.
“The Marzal was not developed as a production car. If you present a car like the Marzal at automobile shows such as Geneva, Turin, and Frankfurt, all the magazines report on the first page about it. You would rather spend 100 million lire for building such an automobile which is still less expensive than paying for all the advertising. That would cost almost a billion lire. So it compensates in any case to build such a throwaway car.”

The Marzal interior is entirely upholstered in silver-colored leather.
Lamborghini Marzal Specifications
The rear-engine and rear-wheel-drive Marzal was a relative lightweight at 2,960 pounds on a 103.1-inch wheelbase. It was 14.6 feet long (175.2 inches) and stood 43.3 inches tall by 66.9 inches wide. The concept car shared a chassis, suspension, steering, and brakes with the Miura.
The Marzal is powered by half of the Lamborghini 4.0-liter V-12 engine. The 175-horsepower, 2.0-liter inline-six-cylinder engine produced peak torque of 132 foot-pounds at 4,600 rpm. Top speed was estimated at 118 miles per hour (190 kmh).

Lamborghini President Ferruccio Lamborghini had the Marzal created as a concept for a true four-seat grand touring car.
Lamborghini Marzal History
The Lamborghini Marzal made its public debut at the 1967 Monaco Grand Prix. Prince Rainier III, accompanied by his wife, Princess Grace, drove the car on his traditional parade lap before the start of the race.
The car made a second public appearance at the 1996 Concorso Italiano in Monterey, Calif., in honor of Carrozzeria Bertone. The Bertone-designed Lamborghini Athon concept was also exhibited at the ’96 Concorso Italiano.
Later the Athon was driven by Prince Albert II during the opening ceremony of the 2018 Historic Grand Prix of Monaco.
The Marzal had been maintained in the Bertone Design Study Museum until it closed in 2014. The Marzal was then sold at RM Sotheby’s Villa d’Este auction on May 21, 2011, for $1,750,449.96 (1,512,000 Euros) including buyer’s premium.

The Lamborghini Marzal at the 1967 Monaco Grand Prix.
Lamborghini Marzal Lap of Honor
On May 7, 1967, shortly before the Monte Carlo Formula 1 Grand Prix, His Serene Highness Rainier III, Prince of Monaco, completed the lap of honor on the track in a legendary car: the Lamborghini Marzal. Its glazed gullwing doors provided an almost unimpeded view of the interior and the silver leather upholstery.
Princess Grace sat in the passenger seat, next to Prince Rainier. Photos of the couple in the Marzal traveled all around the world, turning this unique car into a legend.
Fifty-one years since its first track appearance, the Lamborghini Marzal was displayed at the Grand Prix de Monaco Historique. Lamborghini Polo Storico, celebrating its history with several laps on the same roads as in 1967.

The Lamborghini Marzal and Espada as displayed at the 2018 Grand Prix of Monaco.